Security audit is a detailed analysis of your infrastructure aimed at identifying potential vulnerabilities and unsafe practices.
Code simplifies the auditing process with audit events, which allow you to track a wide range of activities happening in the system.
Purpose and scope
The security event logging mechanism (audit events) is used to:
- Record user and administrator actions related to system configuration changes.
- Register information security incidents.
- Provide the ability to investigate incidents and reconstruct a complete picture of actions in the system.
The scope of application is all levels of the Code platform — from individual projects and groups to instance configuration.
Events are recorded regardless of user role (if they have the right to perform the action) and stored centrally.
Technical capabilities for event logging
The audit system features the following capabilities:
- Centralized event logging: All events are stored in a single audit log.
- Real-time collection: Events are logged instantly at the time of business operation execution. This includes, for example, user login, email change, or enabling
force pushin a protected branch. - Integrity protection: The audit log is read-only for administrators. Logged events can’t be deleted or modified.
- Access via UI or API: Events can be viewed and filtered both in the administrator interface and through the dedicated API.
Use cases
Audit events let you track:
- Who and when changed a user’s access level in a Code project.
- Cases of user creation and deletion.
- Traces of suspicious activity — for example, cases of a bulk employee email change or a repository deletion.
- Changes made to CI/CD environment variables.
- Changes to project and group visibility levels.
Audit events help you:
- Assess risks and strengthen security measures.
- Respond promptly to incidents.
Accessing audit events
Accessing via UI
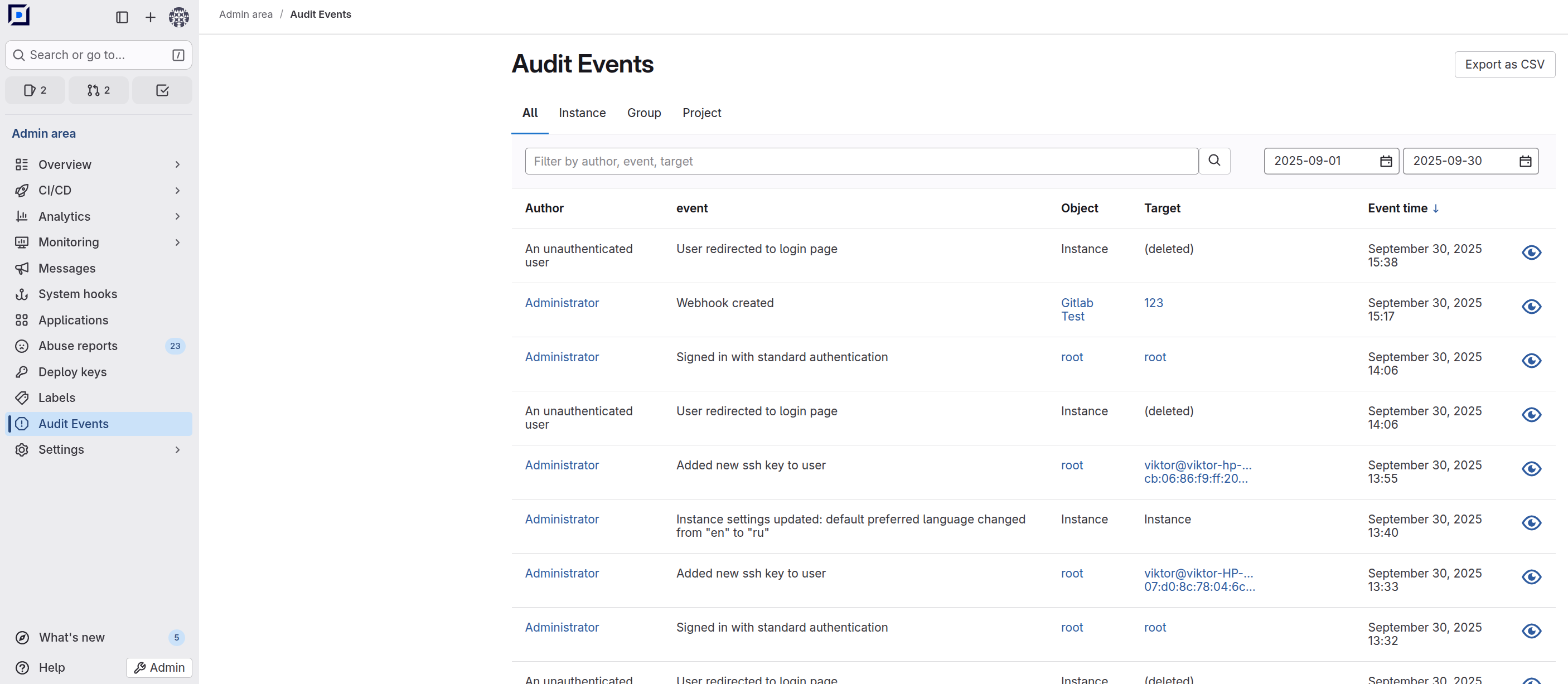
To access audit events, switch to the admin mode and select “Audit events” in the sidebar. This opens the audit event table.
Description of the table columns:
- Author: User who triggered the event.
- Event: System message with event details.
- Object: Related scope of the event (instance, user, group, or project name).
- Target: Entity that was changed (project, user, protected branch, token, or CI variable name, etc.).
- Event time: Date and time when the event occurred.
Accessing via API
Deckhouse Code provides the following API method to retrieve the list of audit events:
POST /api/v4/admin/audit_events/search
The method supports filtering by dates, full-text search, and entity types.
The date range must be within a single calendar month. If created_after and created_before belong to different months, the created_before value will be automatically adjusted to the last day of the month of created_after.
Request parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
created_after |
String | No | Start date (inclusive) in ISO8601 format. Default: beginning of the current month. |
created_before |
String | No | End date (inclusive) in ISO8601 format. Default: end of the current month. |
q |
String | No | Full-text search in the event message. |
sort |
String | No | Sort by creation date. Possible values: created_asc, created_desc (default). |
entity_types |
Array | No | List of entity types for filtering: User, Project, Group, Gitlab::Audit::InstanceScope. |
Example request:
curl --request POST "https://example.com/api/v4/admin/audit_events/search" \
--header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: <your_access_token>" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{
"created_after": "2025-08-01",
"created_before": "2025-08-31",
"q": "repository",
"sort": "created_desc",
"entity_types": ["Project"]
}'
Audit event contents
Each audit event contains a date, time, IP address and user account details, as well as all required information about the scope of changes, object, and what exactly has been changed.
List of audit events
The table below shows example system messages.
Audit events in a production environment contain full information either directly in the message or in an additional JSON field with data.
| Name | System message | Purpose | Audited attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
2fa_login_failed |
User 2fa login failed | A failed attempt to log in with two-factor authentication was detected. | |
access_approved |
User access was approved | User's access request to the instance was approved. | |
access_token_created |
Project/Group access token created | An access token for a project or group was created. | |
access_token_revoked |
Project/Group access token revoked | An access token was revoked. | |
added_gpg_key |
Added new gpg key to user | A user added a new GPG key. | |
added_ssh_key |
User added new ssh key | A user added a new SSH key. | |
application_created |
Application was created | A new application (OAuth or integration) was created. | |
application_deleted |
Application deleted | An application was deleted. | |
application_secret_renew |
Application secret renew | The application secret was renewed. | |
application_updated |
Application Updated | Application parameters were updated. | |
ci_cd_job_token_removed_from_allowlist |
Disallow group to use job token | A project restricted a specific group from using CI/CD Job Token. | |
ci_cd_job_token_added_to_allowlist |
Allow group to use job token | A project allowed a specific group to use CI/CD Job Token. | |
ci_variable_created |
Ci variable #{key} created |
A new CI/CD variable was created. | |
ci_variable_deleted |
Ci variable #{key} deleted |
A CI/CD variable was deleted. | |
ci_variable_updated |
Ci variable updated (Value, Protected) | The value or protection status of a CI/CD variable was updated. | |
deploy_key_created |
Deploy key added | A new deploy key was added for a project or instance. | |
deploy_key_deleted |
Deploy key was deleted | A deploy key was deleted. | |
deploy_key_disabled |
Deploy key disabled | A deploy key was disabled. | |
deploy_key_enabled |
Deploy key enabled | A deploy key was re-enabled. | |
deploy_token_created |
Deploy token created | A deploy token was created for data access. | |
deploy_token_deleted |
Deploy token deleted | A deploy token was deleted. | |
deploy_token_revoked |
Deploy token revoked | A deploy token was revoked by a user or the system. | |
feature_flag_created |
Created feature flag with description | A new feature flag was created. | |
feature_flag_deleted |
Feature flag was deleted | A feature flag was deleted. | |
feature_flag_updated |
Feature flag was updated | A feature flag was updated. | |
group_created |
Group was created | A new group was created. | |
group_export_created |
Group file export was created | A group export file was generated. | |
group_invite_via_group_link_created |
Invited group to group | Another group was invited to the group using a group link. | |
group_invite_via_group_link_deleted |
Revoked group from group | Group access through a group link was revoked. | |
group_invite_via_group_link_updated |
Group access changed | Group access parameters through a group link were updated. | |
group_invite_via_project_group_link_created |
Invited group to project | A group was invited to a project using a group link. | |
group_invite_via_project_group_link_deleted |
Revoked group from project | Group access to a project was revoked. | |
group_invite_via_project_group_link_updated |
Group access for project changed | Group access parameters to a project were updated. | |
group_updated |
Group updated (visibility, 2FA grace period) | Changes in group settings (visibility, security, limits, access policy). |
|
impersonation_initiated |
User root impersonated another user | An administrator started a session impersonating another user. | |
impersonation_stopped |
User root stopped impersonation | An administrator stopped impersonating another user. | |
instance_settings_updated |
Instance settings updated: Signup enabled turned on | Global instance settings were updated. | All instance settings except encrypted fields. |
login_failed |
Attempt to login failed | A login attempt failed. | |
manually_trigger_housekeeping |
Housekeeping task | A housekeeping task for a repository was triggered manually. | |
member_permissions_created |
New member access granted | A user was granted membership (role) in a group or project. | |
member_permissions_destroyed |
Member access revoked | A user's membership was revoked from a group or project. | |
member_permissions_updated |
Member access updated | A user's role or membership expiration date was updated. | |
merge_request_closed_by_project_bot |
Merge request #{merge_request.title} closed by project bot |
A merge request was closed by a project bot. | |
merge_request_created_by_project_bot |
Merge request #{merge_request.title} created by project bot |
A merge request was created by a project bot. | |
merge_request_merged_by_project_bot |
Merge request #{merge_request.title} merged by project bot |
A merge request was merged by a project bot. | |
merge_request_reopened_by_project_bot |
Merge request #{merge_request.title} reopened by project bot |
A merge request was reopened by a project bot. | |
omniauth_login_failed |
Omniauth login failed for #{user} #{provider} |
Failed login attempt via external OAuth/Omniauth provider. | |
password_reset_failed |
Password reset failed | Failed password reset attempt by a user. | |
personal_access_token_issued |
Personal access token issued | A new personal access token was issued. | |
personal_access_token_revoked |
Personal access token revoked | A personal access token was revoked. | |
pipeline_deleted |
Pipeline deleted | A CI/CD pipeline was deleted. | |
project_blobs_removal |
Project blobs removed | Bulk removal of repository blobs in a project. | |
project_created |
Project was created | A new project was created. | |
project_default_branch_changed |
Project default branch updated | The default branch of a project was changed. | |
project_export_created |
Project export created | A project export file was generated. | |
project_feature_updated |
Project features updated | Feature access levels for a project were updated (issues, wiki, etc.). | |
project_setting_updated |
Project settings updated | Project merge commit and squash commit templates were updated. | |
project_text_replacement |
Project text replaced | Bulk text replacement in a project. | |
project_topic_changed |
Project topic changed | Project topic was updated. | |
project_updated |
Project updated (name, namespace) | Project settings were updated (name, namespace, policies). |
|
protected_branch_created |
Protected branch created | A protected branch was created. | |
protected_branch_deleted |
Protected branch was deleted | A protected branch was deleted. | |
protected_branch_updated |
Protected branch was updated | Protected branch rules were updated. | |
protected_tag_created |
Protected tag created | A protected tag was created. | |
protected_tag_deleted |
Protected tag was deleted | A protected tag was deleted. | |
protected_tag_updated |
Protected tag updated | Protected tag rules were updated. | |
removed_gpg_key |
Removed gpg key from user | A user's GPG key was removed. | |
removed_ssh_key |
User removed ssh key | A user's SSH key was removed. | |
requested_password_reset |
User requested password change | A user requested a password reset. | |
revoked_gpg_key |
Revoked gpg key from user | A user's GPG key was revoked. | |
unban_user |
User was unban | A user was unbanned. | |
unblock_user |
User was unblocked | A user was unblocked. | |
user_access_locked |
User access locked | A user account was locked. | |
user_access_unlocked |
User access unlocked | A user account was unlocked. | |
user_activated |
User was activated | A user account was activated. | |
user_banned |
User was banned | A user account was banned. | |
user_blocked |
User was blocked | A user account was blocked. | |
user_created |
User was created | A new user account was created. | |
user_deactivated |
User was deactivated | A user account was deactivated. | |
user_destroyed |
User was destroyed | A user account was deleted. | |
user_email_updated |
User email updated | A user's email address was updated. | |
user_logged_in |
User logged in | A user logged in successfully. | |
user_password_updated |
Password updated | A user's password was changed. | |
user_rejected |
User was rejected | A user account was rejected (for example, during a registration). | |
user_removed_two_factor |
Two factor disabled | A user disabled two-factor authentication. | |
user_settings_updated |
User settings updated | A user updated their profile settings. |
|
user_signup |
User was registered | A new user registered. | |
user_switched_to_admin_mode |
User switched to admin mode | A user switched to admin mode. | |
user_username_updated |
Username updated | A user's username was updated. | |
webhook_created |
Webhook was created | A webhook for a project, group, or instance was created. | |
webhook_destroyed |
System hook removed | A webhook was removed. | |
group_deleted |
Group was deleted | A group was deleted. | |
project_deleted |
Project was deleted | A project was deleted. | |
logout |
User logged out | A user logged out of the system. | |
unauthenticated_session |
Redirected to login | An unauthenticated user was redirected to the login page. | |
ci_runners_bulk_deleted |
CI runner bulk deleted: Errors: | Multiple CI runners were deleted. | |
ci_runner_registered |
CI runner created via API | A CI runner was registered via API. | |
ci_runner_unregistered |
CI runner unregistered | A CI runner was unregistered. | |
ci_runner_token_reset |
CI runner registration token reset | A CI runner's registration token was reset. | |
ci_runner_assigned_to_project |
CI runner assigned to project | A CI runner was assigned to a project. | |
ci_runner_unassigned_from_project |
CI runner unassigned from project | A CI runner was unassigned from a project. | |
ci_runner_created |
CI runner created via UI | A CI runner was created via the user interface. | |
package_registry_package_published |
#{name} package version #{version} has been published |
A new package was published to the package registry. | |
package_registry_package_deleted |
package version #{package.version} has been deleted |
A package was deleted from the package registry. | |
group_access_token_destroyed |
Group access token destroyed | A group access token was destroyed. | |
group_access_token_revoked |
Group access token revoked | A group access token was revoked. | |
personal_access_token_destroyed |
Personal access token destroyed | A personal access token was destroyed. | |
project_access_token_destroyed |
Project access token destroyed | A project access token was destroyed. | |
project_access_token_revoked |
Project access token revoked | A project access token was revoked. | |
approval_rule_created |
Merge request\Project\Group approval rule created | A merge request, project, or group approval rule was created. | |
approval_rule_updated |
Merge request\Project\Group approval rule updated | A merge request, project, or group approval rule was updated. | |
approval_rule_deleted |
Merge request\Project\Group approval rule deleted | A merge request, project, or group approval rule was deleted. | |
approval_rule_propagated |
Approval rules #{rule_names} propagated to #{project_and_group_names} |
Approval rules were propagated to these projects and groups. | |
variable_viewed_api |
User viewed all CI/CD variables via API for this scope or User viewed CI/CD variable #{variable.key} via API |
All CI/CD variables were viewed via API for this scope or A CI/CD variable #{variable.key} was viewed via API. |
|
group_unarchived |
User unarchived group | A group was unarchived. | |
group_archived |
User archived group | A group was archived. | |
comment_deleted |
Comment deleted | A comment was deleted. | |
comment_created |
Comment created | A comment was created. | |
comment_updated |
Comment updated | A comment was updated. | |
user_records_migrated_to_ghost |
User records migrated to ghost | User records were migrated to a ghost user. | |
user_enable_passkey |
User enable new passkey | A new passkey was enabled. | |
user_disable_passkey |
User disable passkey | A passkey was disabled. | |
push_rule_propagated |
Push rule propagated | A push rule was propagated. | |
push_rule_updated |
Push rule updated | An existing push rule was updated. |