The module lifecycle stage: General Availability
Getting started
Here is minimum required configuration(so-called happy path) to get Deckhouse Code running and ready
Minimum requirements
The following requirements must be met to run the Code module:
Deckhouse cluster resources
Minimum resources are calculated for 100 users (the minimum supported spec.scaling.targetUserCount):
| Requests | Limits |
|---|---|
| 7 CPU / 13 Gb | 11 CPU / 17 Gb |
For high availability (HA) installations, plan for at least double the resources.
For more details on scaling, refer to the scaling documentation.
External dependencies
- PostgreSQL version 17 or higher
- Redis version 7.0 or higher
- S3 storage (
YCloudorGenericproviders)
Other components
- A StorageClass for storing Git repositories (
gitData.storageClassparameter) - An IngressClass for routing external traffic to the Code web interface
Enable module
Enable the code module in your Deckhouse Kubernetes Cluster to get code-operator installed. You might use ModuleConfig to achieve that. Example below:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1alpha1
kind: ModuleConfig
metadata:
name: code
spec:
enabled: true # whether to enable this module or not
version: 1
settings:
logLevel: InfoConfigure dependencies
You need to install and configure dependencies: postgres, redis and s3 storage.
Few configuration notices:
- Postgres
- Deckhouse Code requires 2 different databases to be provided from postgres cluster: main and the small one for praefect component
- Postgres extensions to be enabled:
btree_gist,pg_trgm,plpgsql - Connections per user should be not less than 150
- More information and examples are here
- Redis
- Supports either direct connection or sentinels (Sentinel level authorization is not supported, only node level)
- More information and examples are here
- S3 storage
- User policy must contain following permissions:
s3:ListAllMyBuckets,s3:ListBucket,s3:GetObject,s3:PutObject,s3:DeleteObject - If provided credentials don’t have enough permissions to create needed buckets, then they required to be created manually.
Default s3 bucket names are below:
- d8-code-artifacts
- d8-code-ci-secure-files
- d8-code-mr-diffs
- d8-code-git-lfs
- d8-code-packages
- d8-code-terraform-state
- d8-code-uploads
- d8-code-pages (if pages is enabled)
- d8-code-registry (if registry is enabled)
- d8-code-backups (if backup is enabled)
- d8-code-tmp (if backup is enabled)
- More information and examples are here
- User policy must contain following permissions:
Prepare Kubernetes nodes
Managing placement of Deckhouse components
By default, CRD resources are placed on nodes with label node-role.deckhouse.io/code=.
To disable this behaviour set spec.placement.dedicated: false in CodeInstance resource.
Apply CodeInstance custom resource
code-operator handles installation and configuration of Deckhouse Code based on CodeInstance custom resource. Example below:
Currently, the system supports only one
CodeInstance, and it must be namedcode(see example below).
Note that passwords must be enclosed in double quotes.
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: CodeInstance
metadata:
name: code
spec:
scaling:
targetUserCount: 100
storages:
s3: # only external is supported for now
mode: External
external:
provider: YCloud # Generic
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>" # accessKey of SA having access to S3
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>" # secretKey of SA having access to S3
postgres: # only external is supported for now
mode: External
external:
host: <REPLACE_ME> # URL of postgres-master node
port: 5432 # might differ depending on your postgres settings
database: <REPLACE_ME> # database name
username: <REPLACE_ME> # database username
password: "<REPLACE_ME>" # database password in plain text
praefectDatabase: "<REPLACE_ME>" # name of praefect database
praefectUsername: <REPLACE_ME> # username for praefect database
praefectPassword: "<REPLACE_ME>" # password for praefect database
redis: # only external is supported for now
mode: External
external:
host: <REPLACE_ME> # for raw redis cluster. Host URL
port: 6379
auth:
enabled: true
password: "<REPLACE_ME>" # password in plain text
gitData:
storageClass: <REPLACE_ME> # storage class available for your setup
storagePerReplicaGb: 10Verify CodeInstance is applied correctly
To verify that the module started correctly, follow these steps:
-
Check the operator logs for errors:
kubectl -n d8-code logs deploy/code-operator | grep errorYou may see a message about a missing PostgreSQL extension:
"controller-runtime.reconcile.preflight-shared","message":"Missing required extensions: [btree_gin]"This message is not critical and can be safely ignored.
-
Check the status of migration pods:
kubectl -n d8-code get pods | grep migration-vAll pods should have the
Completedstatus. -
Check the status of all other pods in the
d8-codenamespace:kubectl -n d8-code get podsAll pods except those with the
migration-prefix should have theRunningstatus.
Pod startup time depends on your Deckhouse cluster’s capacity and resources. On average, it takes 3–4 minutes.
First launch
Create DNS records
-
If
spec.network.web.hostnameis not set inCodeInstance, the web interface will be available at the address based on Deckhouse global settings:code.company.my. -
If
spec.network.web.hostnameis set inCodeInstance, the web interface will be available at that address. Create an A-type DNS record pointing to the IP address of the Ingress controller servingcode. To find the IP address of the Ingress controller, run:kubectl -n d8-code get ingress webservice-default. -
For advanced
CodeInstanceconfigurations, refer to the network documentation.
Get the root password for Code
kubectl -n d8-code get secret initial-root-password -oyaml | yq .data.password | base64 -dThis command outputs the password for the root user.
Other section
CodeInstance custom resource provides much more configuration options to consider. All of them are described in openapi-spec.
Let’s walk through each root-level CR key and get high-level description of their purposes.
Network
All sort of network-related configuration issues addressed at this section. You can specify custom CA certificates, overwrite ingress hostnames, manage HAProxy loadbalancer in front of the app and much more depending on your cluster configuration Refer to this page to get more details.
GitData
Deckhouse code uses gitaly to store your git repositories. All settings related to how repositories storage configured are stored here.
Backup
Adhoc and regular backups to s3 support. All configurations related to backup/restore process are here. Kindly check also this doc to get more information on how backup/restore process goes.
Scaling
Scaling support. All vertical and horizontal scaling properties are stored here. Vertical scaling stands for number of active users the app capable to process and horizontal scaling primarly stands for high availability and fault tolerance. Refer here for more details
AppConfig
We exposed some gitlab config-file properties AS-IS to our CodeInstance custom resource. All of them are under this section.
Features
Additionally, such features as pages, registry and incoming/outgoing/service_desk email support provided.
Their configuration options available here.
Please also check this doc to get more information on how to configure auth
Code components overview
Section provides high-level overview of existing components and their functions
- Gitaly - git RPC service for handling all Git calls made by GitLab
- Praefect - a transparent proxy between any Git client and Gitaly storage nodes.
- Sidekiq - background jobs processor
- Webservice - exposes product UI and public API
- Shell - a program designed at GitLab to handle SSH-based git sessions, and modifies the list of authorized keys
- Toolbox - a swiss-knife that enables administrators to do restore from backups or use rails-console
- Exporter - process designed in house that allows us to export metrics about Code application internals to Prometheus
- Migrations-job - job that does database migrations
- Backup - cronjob - cronjob responsible for backup process. Optional component
- Pages - a feature that allows you to publish static websites directly from a repository in GitLab. Optional component
- Registry - Container registry, allows pushing and pulling of images. Optional component
- HAProxy - if used, serves as single entry proxy for all ingress traffic. Optional component
Bolded are mandatory components
To learn more about specific components and their purposes you can do here in official documentation.
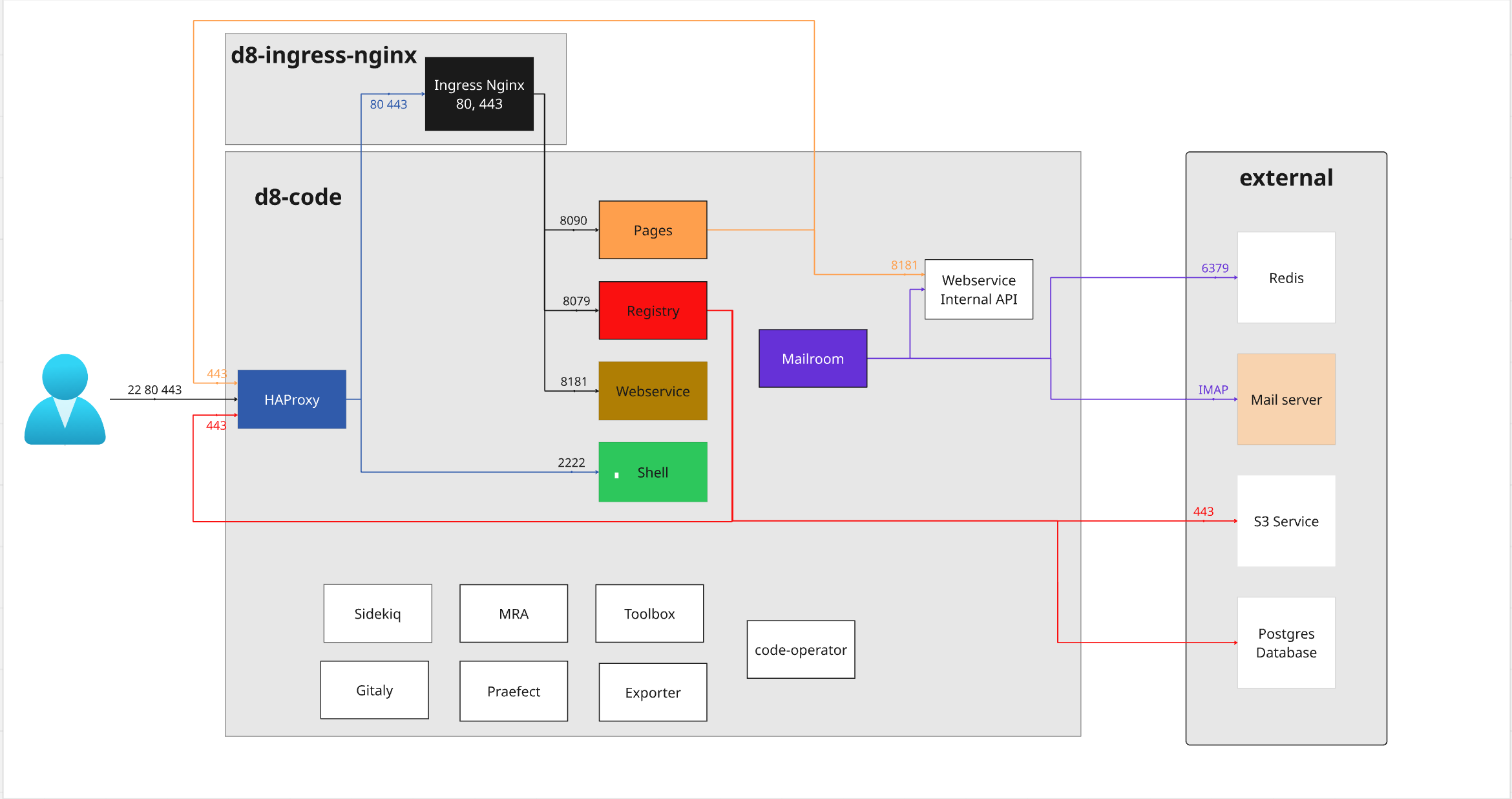
Code components schema
Minimal setup
Only mandatory components included
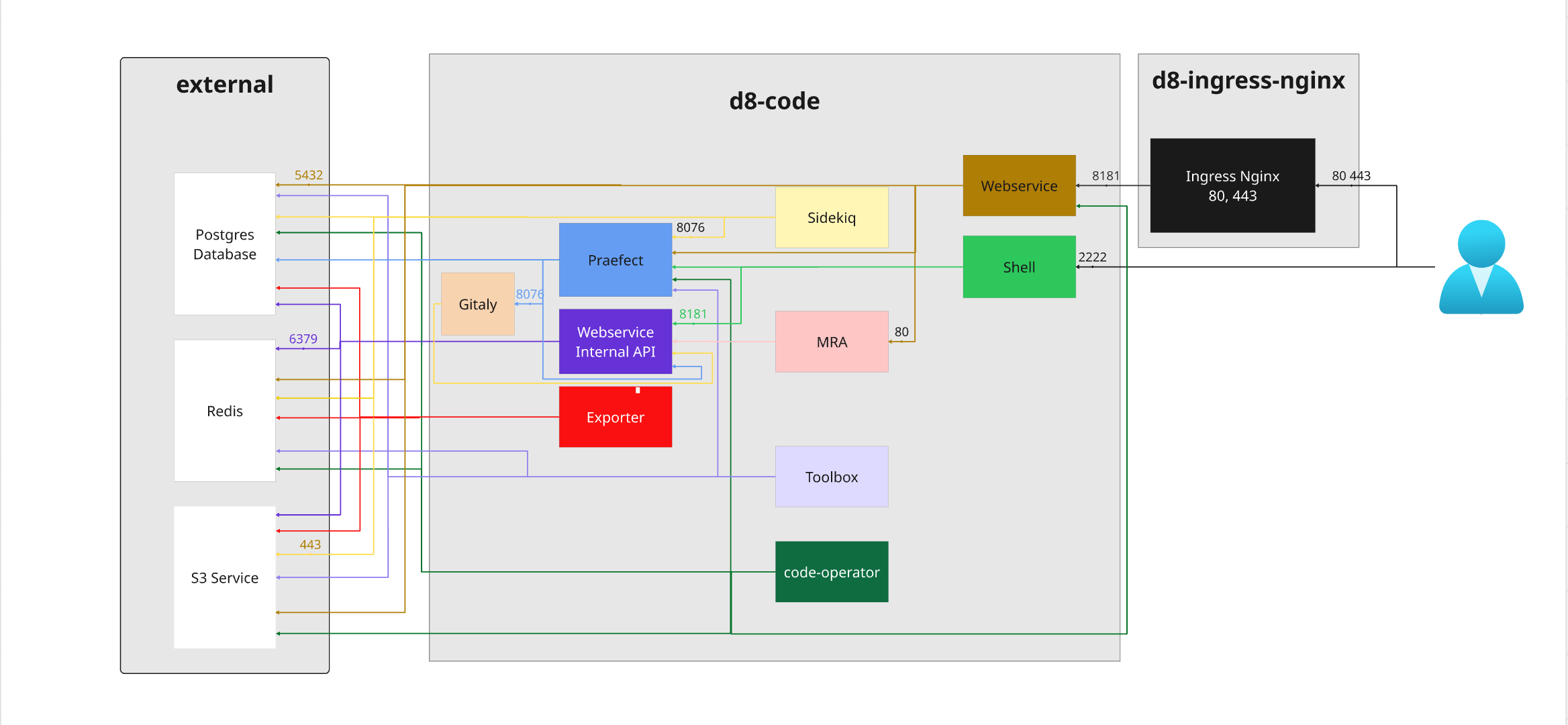
Full setup
All optional components included