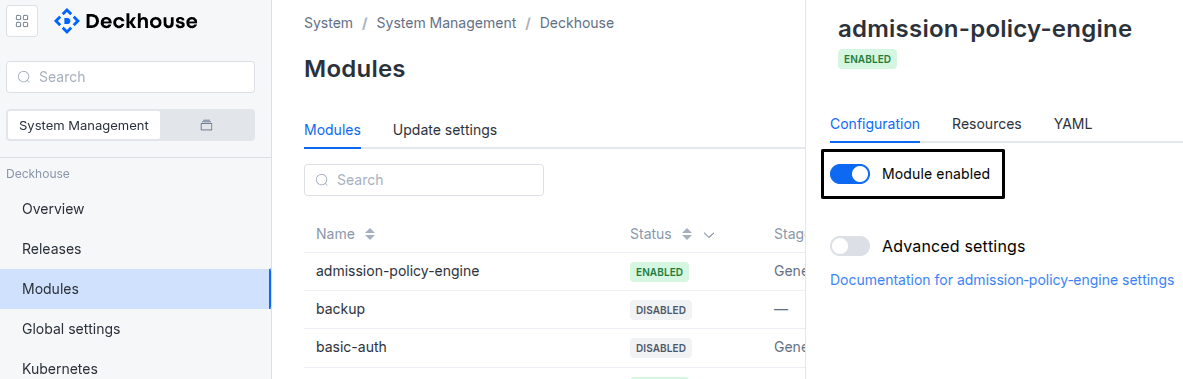
The module lifecycle stage: General Availability
Available with limitations in: CE, BE, SE
Available without limitations in: SE+, EE
Requirements
To the Deckhouse version: 1.68 and above.
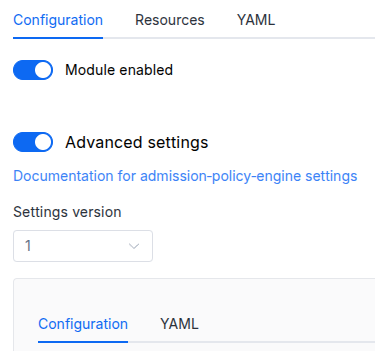
Parameters
Schema version: 1
-
-
objectsettings.authAuthentication configuration.
Default:
{}-
array of stringssettings.auth.allowedUserGroups
An array of user groups that can access the web UI.
This parameter is used if the user-authn module is enabled or the
externalAuthenticationparameter is set.Caution! Note that you must add those groups to the appropriate field in the DexProvider config if this module is used together with the user-authn one.
-
objectsettings.auth.externalAuthentication
Parameters to enable external authentication. Uses Nginx Ingress external-auth mechanism which is based on the the Nginx auth_request module.
Note! External authentication is enabled automatically if the user-authn module is enabled.
Default:
{}-
stringsettings.auth.externalAuthentication.authSignInURLURL to redirect the user for authentication (if the authentication service returned a non-200 HTTP response code).
-
stringsettings.auth.externalAuthentication.authURLURL of the authentication service. If the user is authenticated, the service should return an HTTP 200 response code.
-
-
stringsettings.auth.passwordDeprecated
This parameter is ignored and will be removed in future releases.
It was used for http authorization of the
adminuser, if the user-authn module was disabled or theexternalAuthenticationparameter was not set.Now the external authentication is required for Deckhouse Commander to function properly.
-
array of stringssettings.auth.whitelistSourceRangesAn array if CIDRs that are allowed to authenticate.
Example:
whitelistSourceRanges: - 1.1.1.1/32
-
-
objectsettings.billingBilling configuration.
Default:
{}-
objectsettings.billing.prometheus
Default:
{}-
integersettings.billing.prometheus.diskSizeGigabytes
Disk size for Prometheus metrics storage in gigabytes.
You should manually specify the desired disk size for the Prometheus metrics storage, but you can increase it later if necessary.
The extended-monitoring module automatically monitors the percentage of used disk space.
CAUTION! If the Prometheus metrics storage becomes full, the billing may stop working.
Default:
10Example:
diskSizeGigabytes: "10" -
stringsettings.billing.prometheus.storageClass
The name of the StorageClass to use for Prometheus metrics storage.
If omitted, the StorageClass of the existing PVC is used. If there is no PVC yet, the StorageClass will be used according to the global storageClass parameter setting.
The
storageClassparameter is only considered when the module is enabled. Changing thestorageClassparameter while the module is enabled will not trigger disk re-provisioning.Example:
storageClass: ceph-ssd
-
-
objectsettings.billing.reports
Default:
{}-
integersettings.billing.reports.diskSizeGigabytes
Disk size for reports storage in gigabytes.
You should manually specify the desired disk size for the reports storage, but you can increase it later if necessary.
The extended-monitoring module automatically monitors the percentage of used disk space.
CAUTION! If the reports storage becomes full, the reports will be unavailable.
Default:
2Example:
diskSizeGigabytes: "2" -
stringsettings.billing.reports.storageClass
The name of the StorageClass to use for reports storage.
If omitted, the StorageClass of the existing PVC is used. If there is no PVC yet, the StorageClass will be used according to the global storageClass parameter setting.
The
storageClassparameter is only considered when the module is enabled. Changing thestorageClassparameter while the module is enabled will not trigger disk re-provisioning.Example:
storageClass: ceph-ssd
-
-
-
objectsettings.featureFlagsA parameter used to control experimental features.
Default:
{} -
booleansettings.highAvailability
Manually enable the high availability mode.
By default, Deckhouse automatically decides whether to enable the HA mode. Click here to learn more about the HA mode for modules.
Examples:
highAvailability: truehighAvailability: false -
objectsettings.https
What certificate type to use with the web UI.
This parameter completely overrides the
global.modules.httpssettings.Examples:
customCertificate: secretName: foobar mode: CustomCertificatecertManager: clusterIssuerName: letsencrypt mode: CertManager-
objectsettings.https.certManager
Default:
{}-
stringsettings.https.certManager.clusterIssuerName
What ClusterIssuer to use for the web UI.
Currently,
letsencrypt,letsencrypt-staging,selfsignedare available. Also, you can define your own.Default:
letsencrypt
-
-
objectsettings.https.customCertificate
Default:
{}-
stringsettings.https.customCertificate.secretName
The name of the secret in the
d8-systemnamespace to use with the web UI.This secret must have the kubernetes.io/tls format.
Default:
false
-
-
stringsettings.https.mode
The HTTPS usage mode:
Disabled— in this mode, the web UI can only be accessed over HTTP. Caution! This mode is not supported. HTTPS is required for the module to function properly. If HTTPS is disabled, the web UI will be unavailable.CertManager— the web UI is accessed over HTTPS using a certificate obtained from a clusterIssuer specified in thecertManager.clusterIssuerNameparameter.CustomCertificate— the web UI is accessed over HTTPS using the certificate from thed8-systemnamespace.OnlyInURI— the web UI will work over HTTP (thinking that there is an external HTTPS load balancer in front that terminates HTTPS traffic). All the links in theuser-authnwill be generated using the HTTPS scheme. Load balancer should provide a redirect from HTTP to HTTPS.
Allowed values:
Disabled,CertManager,CustomCertificate,OnlyInURI
-
-
stringsettings.ingressClass
The class of the Ingress controller used for the web UI.
An optional parameter. By default, the
modules.ingressClassglobal value is used.Pattern:
^[a-z0-9]([-a-z0-9]*[a-z0-9])?(\.[a-z0-9]([-a-z0-9]*[a-z0-9])?)*$Example:
ingressClass: nginx -
objectsettings.nodeSelector
The same as in the Pods’
spec.nodeSelectorparameter in Kubernetes.If the parameter is omitted or
false, it will be determined automatically.Example:
disktype: ssd -
objectsettings.postgres
Default:
{}-
objectsettings.postgres.external
-
objectsettings.postgres.external.credentials
Default:
{}-
stringsettings.postgres.external.credentials.secretName
A username and password secret in namespace
d8-commander. If specified, theuserandpasswordfield is ignored.It is recommended to configure database credentials.
Example of creating a secret:
kubectl -n d8-commander create secret generic postgres-secret --from-literal=username=postgres --from-literal=password=postgresExample:
secretName: postgres-secret
-
-
stringsettings.postgres.external.dbDatabase name
-
stringsettings.postgres.external.host
The server address or multiple addresses separated by commas if the PostgreSQL cluster consists of multiple hosts.
Attention! Server ports are specified in the
portparameter.Examples:
host: host1host: host1,host2,host3 -
stringsettings.postgres.external.passwordDeprecated
User password
This parameter is deprecated, please use
credentials.secretName, which is more secure. -
stringsettings.postgres.external.port
The server port or multiple ports are separated by commas if the PostgreSQL cluster consists of multiple hosts.
Attention! Each server must specify its own port.
Examples:
port: "5432"port: 5432,5432,5433 -
objectsettings.postgres.external.ssl
-
stringsettings.postgres.external.ssl.secretName
The name of the secret in the
d8-commandernamespace which contains client certificate for certificate authentication on the PostgreSQL server.Example of creating a secret:
kubectl -n d8-commander create secret generic postgres-ssl --from-file=tls.crt=client.crt --from-file=tls.key=client.key --from-file=ca.crt=ca.crtExample:
secretName: postgres-ssl
-
-
stringsettings.postgres.external.userDeprecated
User name
This parameter is deprecated, please use
credentials.secretName, which is more secure.Example:
user: postgres
-
-
objectsettings.postgres.internal
Default:
{}-
integersettings.postgres.internal.diskSizeGigabytes
Disk size for PostgreSQL database in gigabytes.
You should manually specify the desired disk size for the PostgreSQL database, but you can increase it later if necessary.
The extended-monitoring module automatically monitors the percentage of used disk space.
CAUTION! If the PostgreSQL data storage becomes full, the application may stop working.
Default:
10 -
stringsettings.postgres.internal.storageClass
The name of the StorageClass to use.
If omitted, the StorageClass of the existing PVC is used. If there is no PVC yet, either the global StorageClass or
global.discovery.defaultStorageClassis used.Refer to the documentation section Changing the storage class if you want to change this value.
Example:
storageClass: ceph-ssd
-
-
stringsettings.postgres.mode
The PostgreSQL usage mode:
-
Internal— PostgreSQL is deployed in a cluster and managed using the postgres-operator.This is not a recommended method for use in production environments. However, the use of
operator-postgresis convenient for quick start with Deckhouse Commander or for environments where there are no high availability and support requirements. -
External- an external PostgreSQL installation managed by the user is used. This is the recommended way to use Deckhouse Commander in production environments.
Default:
InternalAllowed values:
Internal,External -
-
-
array of objectssettings.tolerations
The same as in the Pods’
spec.tolerationsparameter in Kubernetes;If the parameter is omitted or
false, it will be determined automatically.Example:
tolerations: - effect: NoSchedule key: key1 operator: Equal value: value1-
stringsettings.tolerations.effect
-
stringsettings.tolerations.key
-
stringsettings.tolerations.operator
-
integersettings.tolerations.tolerationSeconds
-
stringsettings.tolerations.value
-
-