The module lifecycle stage: General Availability
Feature: Pages
Assuming public domain template is %s.example.com, the Pages will be available at https://code-pages.example.com (code subdomain).
Generic
Example of usage Generic S3 (S3-compatible service) for deployment:
...
features:
pages:
enabled: true
s3:
mode: External
bucketName: d8-code-pages
external:
provider: Generic
region: <REPLACE_ME>
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
endpoint: <REPLACE_ME> # e.g. http://minio.example.com:9090
...
YCloud
Example of usage YCloud S3 for deployment:
...
features:
pages:
enabled: true
s3:
mode: External
bucketName: d8-code-pages
external:
provider: YCloud
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
...
AzureRM
Example of usage AzureRM for deployment:
...
features:
pages:
enabled: true
s3:
mode: External
bucketName: d8-code-pages
external:
provider: AzureRM
azureAccountName: <REPLACE_ME>
azureAccessKey: <REPLACE_ME>
...
External Redis
Examples for different configuration of external redis cluster
Single node
...
storages:
redis:
external:
auth:
enabled: true
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
host: <REPLACE_ME>
port: 6379
mode: External
...
Single node (with TLS)
...
storages:
redis:
external:
auth:
enabled: true
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
host: <REPLACE_ME>
port: 6380
serverCA: <CERTIFICATE>
mode: External
...
With sentinels
Note: Authentication is supported only on Redis servers and is not available on Redis Sentinels.
...
storages:
redis:
external:
auth:
enabled: true
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
masterName: <REPLACE_ME>
port: 6379
sentinels:
- host: <REPLACE_ME> # sentinel host #1
port: 26379
- host: <REPLACE_ME> # sentinel host #2
mode: External
...
With sentinels (with TLS)
Note: Authentication is supported only on Redis servers and is not available on Redis Sentinels.
Warning: Ensure that the Redis servers and Sentinels are configured to work with a TLS certificate.
...
storages:
redis:
external:
auth:
enabled: true
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
masterName: <REPLACE_ME>
port: 6380
serverCA: <CERTIFICATE>
sentinels:
- host: <REPLACE_ME> # sentinel host #1
port: 26380
- host: <REPLACE_ME> # sentinel host #2
mode: External
...
External Postgres
TLS disabled
...
storages:
postgres:
external:
database: db
host: <REPLACE_ME> # master host fqdn
port: 5432
username: <REPLACE_ME>
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
praefectDatabase: praefect
praefectUsername: <REPLACE_ME>
praefectPassword: "<REPLACE_ME>"
mode: External
...
TLS enabled
You can also use TLS authentication for connection to main database:
...
storages:
postgres:
external:
database: db
host: <REPLACE_ME> # master host fqdn
port: 5432
username: <REPLACE_ME>
sslmode: verify-full
serverCA: |
# postgres server CA
clientCert: |
# Your TLS certificate
clientKey: |
# Your TLS key
mode: External
...
External S3
Generic
Example of usage Generic S3 (S3-compatible service):
...
storages:
s3:
mode: External
external:
provider: Generic
region: <REPLACE_ME>
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
endpoint: <REPLACE_ME> # e.g. http://minio.example.com:9090
...
YCloud
Without server-side-encryption
For example of usage YCloud S3 look here
With server-side-encryption
Example of usage AWS with SSE (Server-Side Encryption):
...
storages:
s3:
mode: External
external:
provider: AWS
region: us-west-2
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
storageOptions:
serverSideEncryption: aws:kms
serverSideEncryptionKmsKeyId: <REPLACE_ME> # e.g. arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:111122223333:key/1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-1234567890ab
...
AzureRM
Example of usage AzureRM:
...
storages:
s3:
mode: External
external:
provider: AzureRM
azureAccountName: <REPLACE_ME>
azureAccessKey: <REPLACE_ME>
...
Backups
backup:
enabled: true
cronSchedule: "0 0 1 * *"
s3:
bucketName: <REPLACE_ME>
mode: External
external:
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
provider: <REPLACE_ME>
region: <REPLACE_ME>
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>"
persistentVolumeClaim:
enabled: <true|false>
storageClass: network-hdd
Prepare external resources with YCloud
Setup Managed Service for PostgreSQL
To create a Managed Service for PostgreSQL cluster, you need the vpc.user role and the managed-postgresql.editor role or higher. For more information on assigning roles, see the Identity and Access Management documentation.
In the management console, select the folder where you want to create a DB cluster.
- Select Managed Service for PostgreSQL.
- Click Create cluster.
- Enter a name for the cluster in the Cluster name field. It must be unique within the folder.
- Select the environment where you want to create the cluster (you cannot change the environment once the cluster is created):
PRODUCTION: For stable versions of your apps.PRESTABLE: For testing purposes. The prestable environment is similar to the production environment and likewise covered by the SLA, but it is the first to get new functionalities, improvements, and bug fixes. In the prestable environment, you can test compatibility of new versions with your application.
- Select the DBMS version (16+ recommended).
- Select the host class that defines the technical specifications of the VMs where the DB hosts will be deployed. All available options are listed under Host classes. When you change the host class for a cluster, the characteristics of all the already created hosts change too.
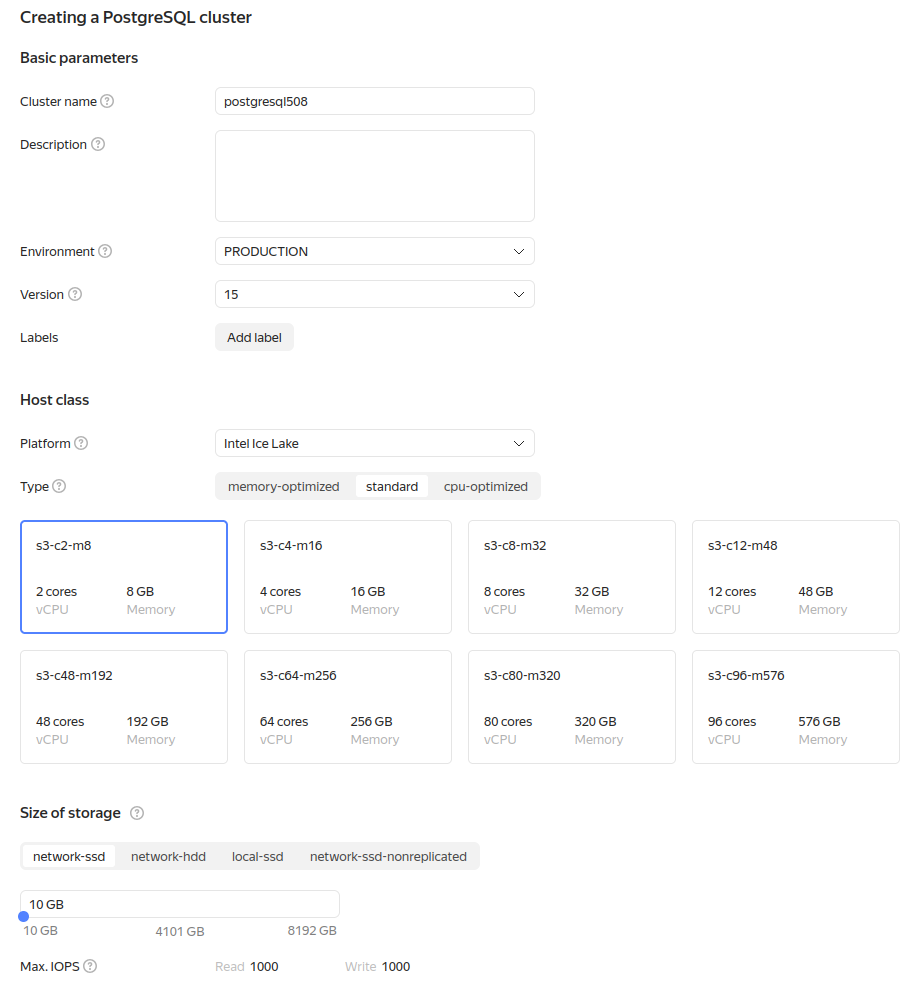
- Under Database, specify the DB attributes:
- DB name. The name must be unique within the folder.
The database name may contain Latin letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens. The name may be up to 63 characters
long. The names
postgres,template0, andtemplate1are reserved for Managed Service for PostgreSQL. You cannot create databases with these names. - DB owner username and password. By default, the new user is assigned 50 connections to each host in the cluster.
- Locale for sorting and character set locale. These settings define the rules for sorting strings (
LC_COLLATE) and classifying characters (LC_CTYPE). In Managed Service for PostgreSQL, locale settings apply at the individual DB level. By default, theClocale is used. For more information about locale settings, see the PostgreSQL documentation.
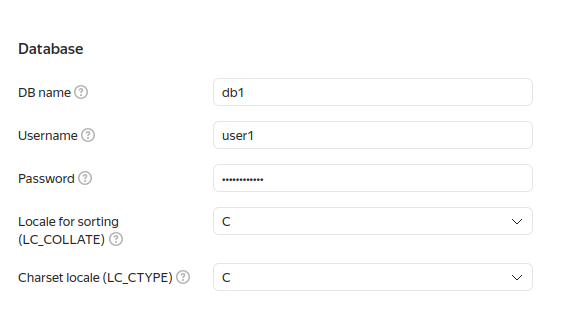
- Click Create cluster.
- It takes sometime to create cluster.
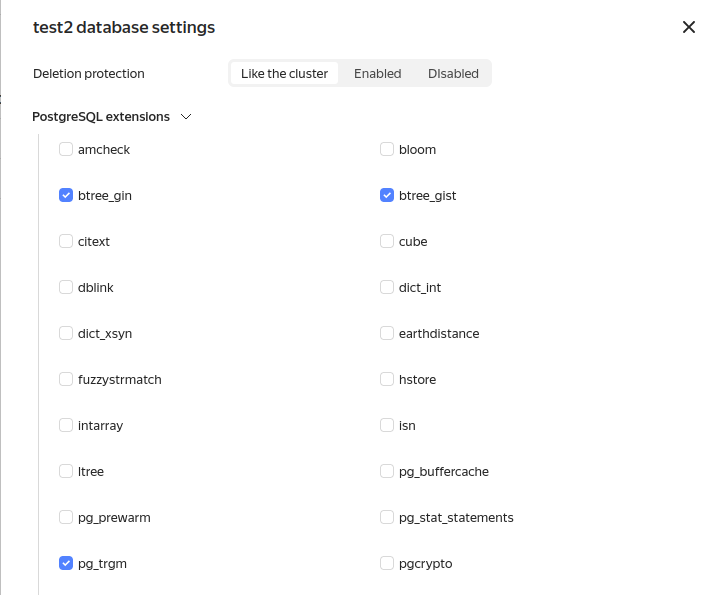
- Click on cluster name and go to Databases tab. Choose database and toggle following extensions:
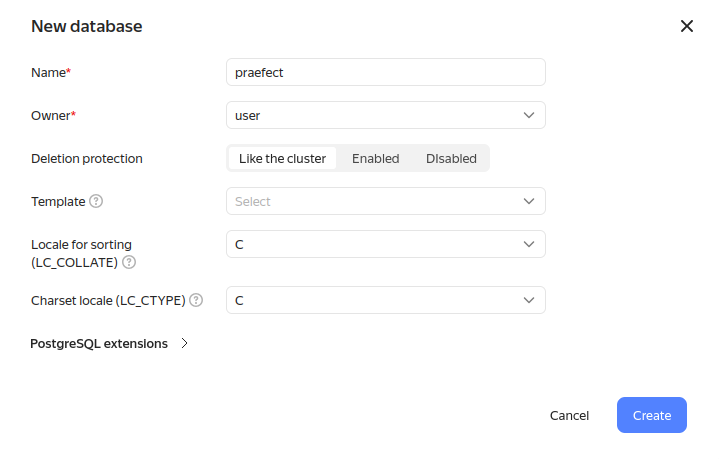
- Add database for Praefect component:
- Go to Users tab and set connection limit. We recommend set at least 150.
Postgres configuration results in snippet
...
storages:
postgres:
mode: External
external:
host: <REPLACE_ME> # YC master host fqdn
port: 6432
database: <REPLACE_ME>
username: <REPLACE_ME>
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
praefectDatabase: praefect
praefectUsername: <REPLACE_ME> # the same as postgres.username
praefectPassword: "<REPLACE_ME>" # the same as postgres.password
...
Setup Managed Service for redis
To create a Managed Service for Redis cluster, you need the vpc.user) role and the managed-redis.editor role or higher. For more information on assigning roles, see the Identity and Access Management documentation.
In the management console, go to the folder to create a DB cluster in.
- Select Managed Service for Redis.
- Click Create cluster.
- Under Basic parameters:
- Enter a name for the cluster in the Cluster name field. It must be unique within the folder.
- (Optional) Add a cluster description.
- Select the environment where you want to create the cluster (you cannot change the environment once the cluster is
created):
PRODUCTION: For stable versions of your apps.PRESTABLE: For testing purposes. The prestable environment is similar to the production environment and likewise covered by the SLA, but it is the first to get new functionalities, improvements, and bug fixes. In the prestable environment, you can test compatibility of new versions with your application.
- Select the DBMS version (recommended 7.0+).
- Click Create cluster.
- It takes sometime to create cluster.
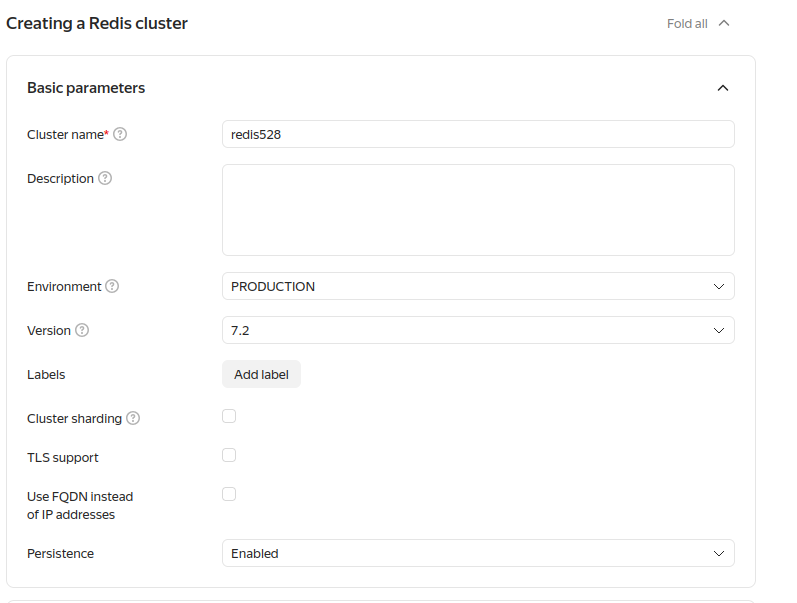
Redis configuration results in snippet
Note: When using a Redis cluster with more than one host, use the example configuration for Redis Sentinels.
...
storages:
redis:
mode: External
external:
host: <REPLACE_ME> # FQDN of master host
port: 6379
auth:
enabled: true
password: "<REPLACE_ME>"
...
Setup S3
Create a user named d8-code-sa. The command response will contain its parameters:
Instruction of creating service account using web page
Example of using YC CLI:
yc iam service-account create --name d8-code-sa
It returns user parameters in response:
id: <userID>
folder_id: <folderID>
created_at: "YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ"
name: d8-code-sa
Assign the storage.editor role to the newly created user:
yc resource-manager folder add-access-binding <folderID> --role storage.editor --subject serviceAccount:<userID>
Create Access key for service account. These parameters will be used to log in to the cloud:
yc iam access-key create --service-account-name d8-code-sa
access_key:
id: <id>
service_account_id: <userID>
created_at: "YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ"
key_id: <ACCESS_KEY>
secret: <SECRET_KEY>
S3 configuration results in snippet
...
features:
pages:
enabled: true
s3:
mode: External
external:
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>" # accesskey.key_id you got at previous step
provider: YCloud
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>" # secretkey you got at previous step
...
storages:
s3:
mode: External
external:
provider: YCloud
accessKey: "<REPLACE_ME>" # accesskey.key_id you got at previous step
secretKey: "<REPLACE_ME>" # secretkey you got at previous step
proxyDownload: true
...
Setup website metrics
Example based on Yandex.Metrica
Add following snippet to CodeInstance:
...
appConfig:
contentSecurityPolicy:
directives:
default_src: "'self'"
img_src: "'self' data: blob: https://mc.yandex.ru https://mc.yandex.com"
script_src: "'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' 'nonce-<SCRIPT_ID>' https://mc.yandex.ru https://mc.yandex.az https://mc.yandex.by https://mc.yandex.co.il https://mc.yandex.com https://mc.yandex.com.am https://mc.yandex.com.ge https://mc.yandex.com.tr https://mc.yandex.ee https://mc.yandex.fr https://mc.yandex.kg https://mc.yandex.kz https://mc.yandex.lt https://mc.yandex.lv https://mc.yandex.md https://mc.yandex.tj https://mc.yandex.tm https://mc.yandex.uz https://mc.webvisor.com https://mc.webvisor.org https://yastatic.net"
connect_src: "'self' https://mc.yandex.ru https://mc.yandex.com"
customHtmlHeaderTags: >
<!-- Yandex.Metrika counter -->
<script type="text/javascript" nonce="<SCRIPT_ID>">
(function(m,e,t,r,i,k,a){m[i]=m[i]||function(){(m[i].a=m[i].a||[]).push(arguments)};
m[i].l=1*new Date();
for (var j = 0; j < document.scripts.length; j++) {if (document.scripts[j].src === r) { return; }}
k=e.createElement(t),a=e.getElementsByTagName(t)[0],k.async=1,k.src=r,a.parentNode.insertBefore(k,a)})
(window, document, "script", "https://mc.yandex.ru/metrika/tag.js", "ym");
ym(100866129, "init", {
clickmap:true,
trackLinks:true,
accurateTrackBounce:true
});
</script>
<noscript><div><img src="https://mc.yandex.ru/watch/<TARGET_ID>"
style="position:absolute; left:-9999px;" alt="" /></div></noscript>
<!-- /Yandex.Metrika counter -->
...
Don’t forget replace <SCRIPT_ID> and <TARGET_ID> with your values.