The module lifecycle stage: General Availability
An example of the module configuration
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1alpha1
kind: ModuleConfig
metadata:
name: prometheus
spec:
version: 2
enabled: true
settings:
auth:
password: xxxxxx
retentionDays: 7
storageClass: rbd
nodeSelector:
node-role/monitoring: ""
tolerations:
- key: dedicated.deckhouse.io
operator: Equal
value: monitoring
Writing Prometheus data to the longterm storage
Prometheus supports remote_write’ing data from the local Prometheus to a separate longterm storage (e.g., VictoriaMetrics). In Deckhouse, this mechanism is implemented using the PrometheusRemoteWrite custom resource.
For VictoriaMetrics detailed information about how to send data to vmagent can be found in the VictoriaMetrics documentation.
Example of the basic PrometheusRemoteWrite
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: PrometheusRemoteWrite
metadata:
name: test-remote-write
spec:
url: https://victoriametrics-test.domain.com/api/v1/write
Example of the expanded PrometheusRemoteWrite
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: PrometheusRemoteWrite
metadata:
name: test-remote-write
spec:
url: https://victoriametrics-test.domain.com/api/v1/write
basicAuth:
username: username
password: password
writeRelabelConfigs:
- sourceLabels: [__name__]
action: keep
regex: prometheus_build_.*|my_cool_app_metrics_.*
- sourceLabels: [__name__]
action: drop
regex: my_cool_app_metrics_with_sensitive_data
Connecting Prometheus to an external Grafana instance
Each ingress-nginx-controller has certificates that can be used to connect to Prometheus. All you need is to create an additional Ingress resource.
For the example below, it is presumed that Secret example-com-tls already exist in namespace d8-monitoring.
Names for Ingress my-prometheus-api and Secret my-basic-auth-secret are there for example. Change them to the most suitable names for your case.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-prometheus-api
namespace: d8-monitoring
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-type: basic
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-secret: my-basic-auth-secret
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/app-root: /graph
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: |
proxy_ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/client.crt;
proxy_ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/client.key;
proxy_ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
proxy_ssl_session_reuse on;
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: prometheus-api.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: prometheus
port:
name: https
path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls:
- hosts:
- prometheus-api.example.com
secretName: example-com-tls
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-basic-auth-secret
namespace: d8-monitoring
type: Opaque
data:
# Basic-auth string is hashed using htpasswd.
auth: Zm9vOiRhcHIxJE9GRzNYeWJwJGNrTDBGSERBa29YWUlsSDkuY3lzVDAK # foo:bar
Next, you only need to add the data source to Grafana:
Specify https://prometheus-api.<cluster-domain> as the URL.
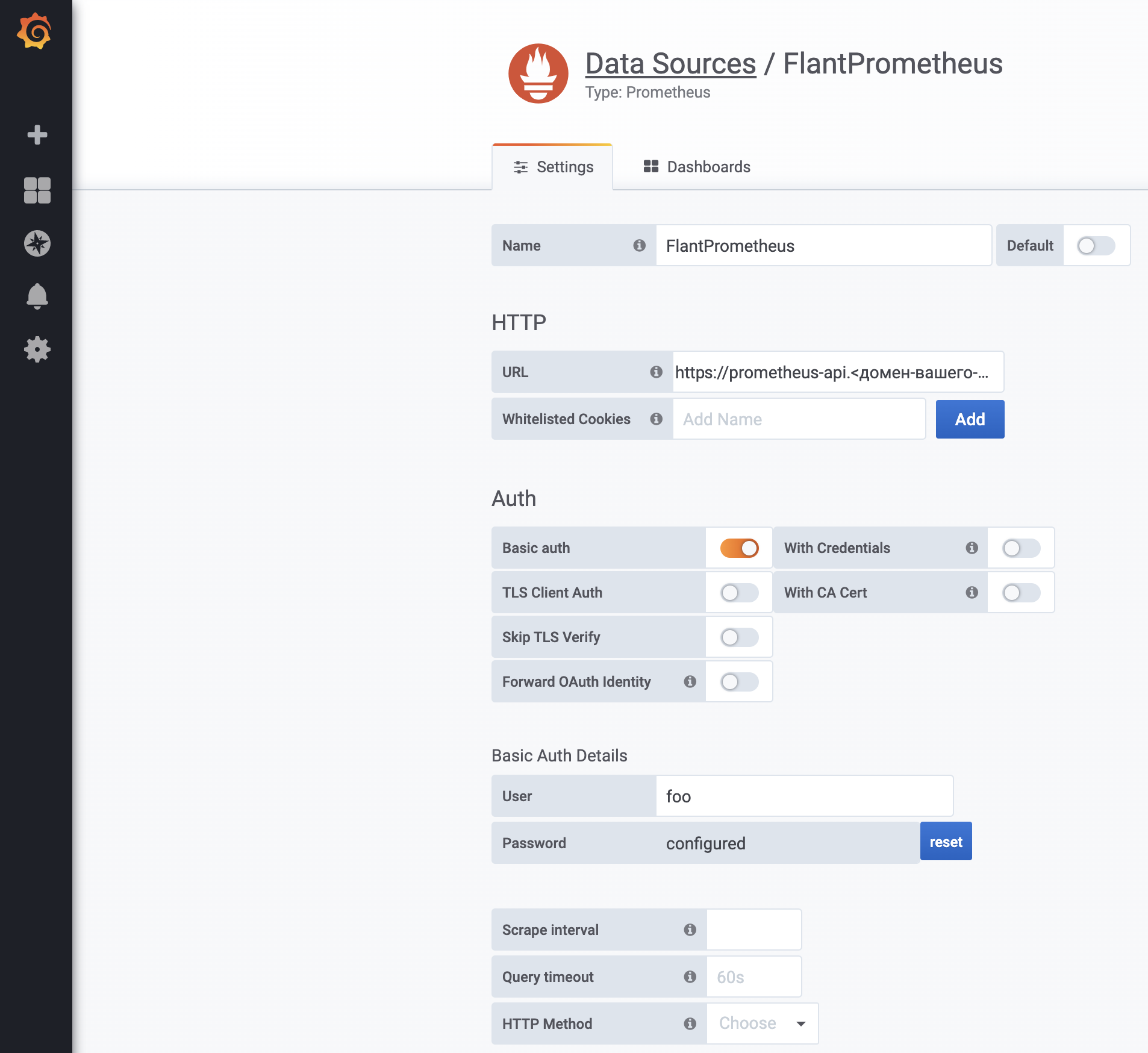
-
Note that basic authorization is not sufficiently secure and safe. You are encouraged to implement additional safety measures, e.g., attach the
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/whitelist-source-rangeannotation. -
It is not recommended connecting this way since you have to create an Ingress resource in the system namespace. Deckhouse does not guarantee the functionality of this connection method due to its regular updates.
-
This Ingress resource can be used to access the Prometheus API not only from Grafana but for other integrations, e.g., the Prometheus federation.
Connecting an external app to Prometheus
The connection to Prometheus is protected using kube-rbac-proxy. To connect, you need to create a ServiceAccount with the necessary permissions.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: app
namespace: default
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: app:prometheus-access
rules:
- apiGroups: ["monitoring.coreos.com"]
resources: ["prometheuses/http"]
resourceNames: ["main", "longterm"]
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: app:prometheus-access
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: app:prometheus-access
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: app
namespace: default
Define the following job containing the curl request:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: app-curl
namespace: default
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: app-curl
spec:
serviceAccountName: app
containers:
- name: app-curl
image: curlimages/curl:7.69.1
command: ["sh", "-c"]
args:
- >-
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token)" -k -f
https://prometheus.d8-monitoring:9090/api/v1/query_range?query=up\&start=1584001500\&end=1584023100\&step=30
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4
The job must complete successfully.
Sending alerts to Telegram
Alertmanager supports sending alerts to Telegram directly.
Create the Secret in the d8-monitoring namespace:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: telegram-bot-secret
namespace: d8-monitoring
stringData:
token: "562696849:AAExcuJ8H6z4pTlPuocbrXXXXXXXXXXXx"
Deploy CustomAlertManager CR:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1alpha1
kind: CustomAlertmanager
metadata:
name: telegram
spec:
type: Internal
internal:
receivers:
- name: telegram
telegramConfigs:
- botToken:
name: telegram-bot-secret
key: token
chatID: -30490XXXXX
route:
groupBy:
- job
groupInterval: 5m
groupWait: 30s
receiver: telegram
repeatInterval: 12h
The fields token in the Secret and chatID in the CustomAlertmanager custom resource must be set on your own. Read more about Telegram API.
Example of sending alerts to Slack with a filter
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1alpha1
kind: CustomAlertmanager
metadata:
name: slack
spec:
internal:
receivers:
- name: devnull
- name: slack
slackConfigs:
- apiURL:
key: apiURL
name: slack-apiurl
channel: {{ dig .Values.werf.env .Values.slack.channel._default .Values.slack.channel }}
fields:
- short: true
title: Severity
value: '{{`{{ .CommonLabels.severity_level }}`}}'
- short: true
title: Status
value: '{{`{{ .Status }}`}}'
- title: Summary
value: '{{`{{ range .Alerts }}`}}{{`{{ .Annotations.summary }}`}} {{`{{ end }}`}}'
- title: Description
value: '{{`{{ range .Alerts }}`}}{{`{{ .Annotations.description }}`}} {{`{{ end }}`}}'
- title: Labels
value: '{{`{{ range .Alerts }}`}} {{`{{ range .Labels.SortedPairs }}`}}{{`{{ printf "%s:
%s\n" .Name .Value }}`}}{{`{{ end }}`}}{{`{{ end }}`}}'
- title: Links
value: '{{`{{ (index .Alerts 0).GeneratorURL }}`}}'
title: '{{`{{ .CommonLabels.alertname }}`}}'
route:
groupBy:
- '...'
receiver: devnull
routes:
- matchers:
- matchType: =~
name: severity_level
value: "^[4-9]$"
receiver: slack
repeatInterval: 12h
type: Internal
Example of sending alerts to Opsgenie
- name: opsgenie
opsgenieConfigs:
- apiKey:
key: data
name: opsgenie
description: |
{{ range .Alerts }}{{ .Annotations.summary }} {{ end }}
{{ range .Alerts }}{{ .Annotations.description }} {{ end }}
message: '{{ .CommonLabels.alertname }}'
priority: P1
responders:
- id: team_id
type: team
Example of sending alert by Email
Create a Secret with base64 encoded password for email account as value of password:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: am-mail-server-pass
namespace: d8-monitoring
data:
password: BASE64_ENCODED_PASSWORD_HERE
Change values in CustomAlertManager manifest as you need and apply the resource:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1alpha1
kind: CustomAlertmanager
metadata:
name: mail
spec:
type: Internal
internal:
receivers:
- name: devnull
- name: mail
emailConfigs:
- to: oncall@example.com
from: prom@example.com
smarthost: mx.example.com:587
authIdentity: prom@example.com
authUsername: prom@example.com
authPassword:
key: password
name: am-mail-server-pass
# In case you have custom TLS certificates, you can put public part of your CA in a ConfigMap and deploy it in d8-monitoring namespace
# tlsConfig:
# insecureSkipVerify: true
# ca:
# configMap:
# key: ca.pem
# name: alertmanager-mail-server-ca
sendResolved: true
requireTLS: true
route:
groupBy:
- job
groupInterval: 5m
groupWait: 30s
receiver: devnull
repeatInterval: 24h
routes:
- matchers:
- matchType: =~
name: severity_level
value: "^[1-4]$"
receiver: mail