Layouts
This section describes the possible node placement layouts in Selectel infrastructure and the related configuration options. The selected layout affects networking behavior, availability of public IP addresses, outgoing traffic routing, and how nodes are accessed.
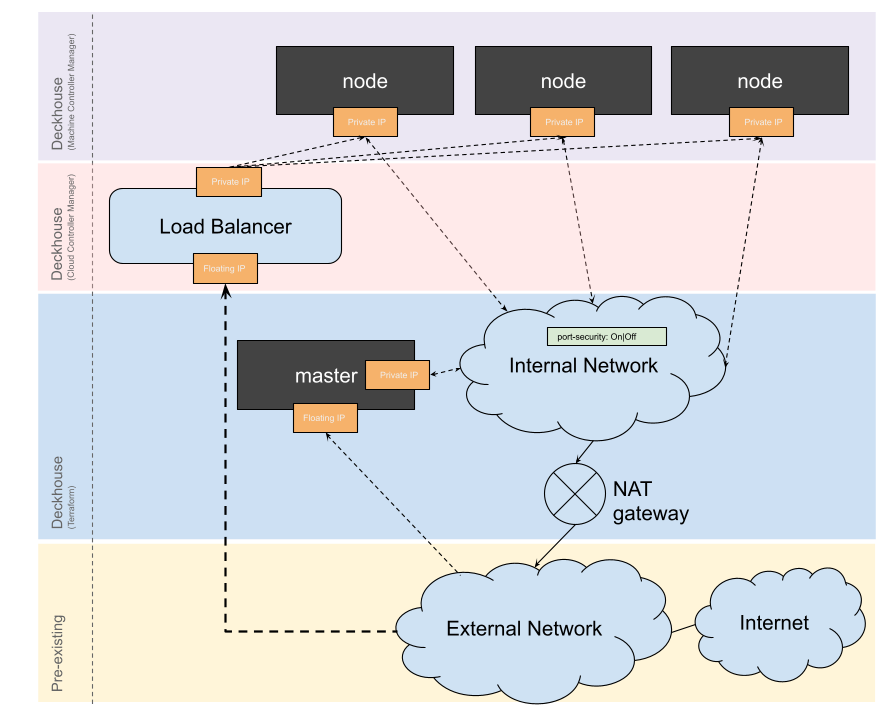
Standard
In this scheme, an internal cluster network is created with a gateway to the public network; the nodes do not have public IP addresses. The floating IP is assigned to the master node.
If the provider does not support SecurityGroups,
all applications running on nodes with Floating IPs assigned will be available at a public IP.
For example, kube-apiserver on master nodes will be available on port 6443.
To avoid this, we recommend using the SimpleWithInternalNetwork or Standard layout
with a bastion host.
Example layout configuration:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: OpenStackClusterConfiguration
layout: Standard
standard:
internalNetworkCIDR: 192.168.199.0/24 # Required.
internalNetworkDNSServers: # Required.
- 8.8.8.8
- 4.2.2.2
internalNetworkSecurity: true|false # Optional, true by default.
externalNetworkName: shared # Required.
bastion:
zone: ru2-b # Optional.
volumeType: fast-ru-2b # Optional.
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.large # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-20-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
rootDiskSize: 50 # Optional, 50 GB by default.
additionalTags:
severity: critical # Optional.
environment: production # Optional.
masterNodeGroup:
replicas: 3
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.large # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 50
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
additionalTags:
severity: critical
environment: production
# Required, volume type map for etcd and Kubernetes certificates
# (always use the fastest disk supplied by the provider).
volumeTypeMap:
# If rootDiskSize is specified, this volume type will
# be also used for master root volume.
ru-1a: fast-ru-1a
ru-1b: fast-ru-1b
ru-1c: fast-ru-1c
nodeGroups:
- name: front
replicas: 2
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.small # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 20
# Optional, false by default. Determines if configuration drive is
# required during vm bootstrap process. It's needed if there
# is no DHCP in the network that is used as a default gateway.
configDrive: false
# Required, the gateway of this network will be used as the default gateway.
# Matches the cloud.prefix in the ClusterConfiguration resource.
mainNetwork: kube
additionalNetworks: # Optional.
- office
- shared
# Optional, if there are networks with disabled port
# security their names must be specified.
networksWithSecurityDisabled:
- office
# Optional, a list of network pools where to order floating IPs.
floatingIPPools:
- public
- shared
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
zones:
- ru-1a
- ru-1b
sshPublicKey: "<SSH_PUBLIC_KEY>"
tags:
project: cms
owner: default
provider:
...
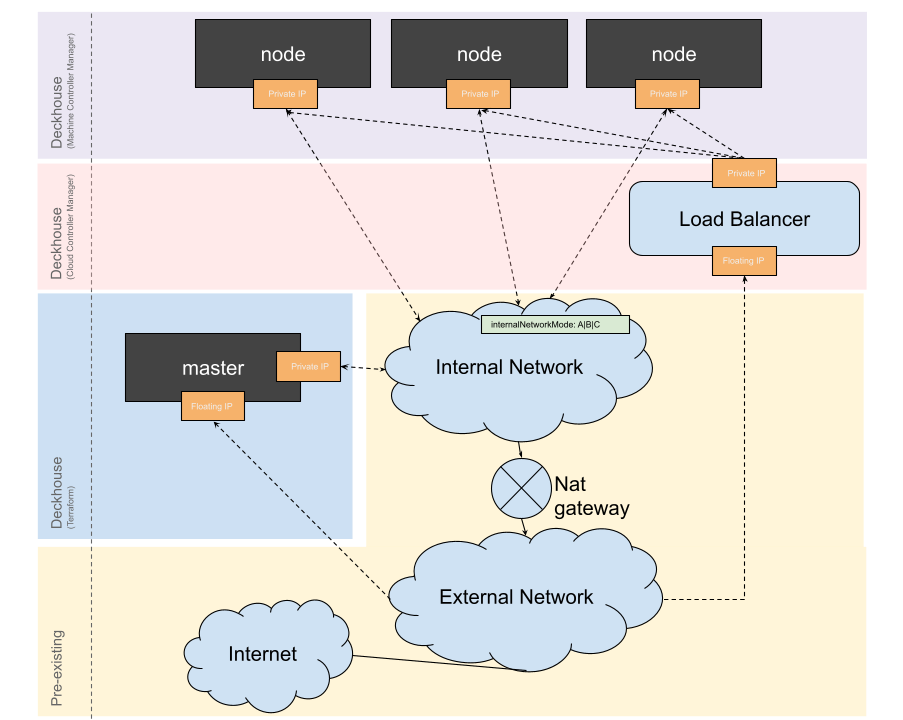
StandardWithNoRouter
An internal cluster network is created that does not have access to the public network. All nodes (including master ones) have two interfaces: the first one to the public network, the second one to the internal network. This layout should be used if you want all nodes in the cluster to be directly accessible.
- This strategy does not support a LoadBalancer since a Floating IP is not available for the router-less network. Thus, you cannot provision a LoadBalancer with the Floating IP. An internal LoadBalancer with the virtual IP in the public network is only accessible from cluster nodes.
- Using this strategy, make sure to explicitly specify the name of the internal network in
additionalNetworkswhen creating an OpenStackInstanceClass in the cluster.
Example layout configuration:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: OpenStackClusterConfiguration
layout: StandardWithNoRouter
standardWithNoRouter:
internalNetworkCIDR: 192.168.199.0/24 # Required.
externalNetworkName: ext-net # Required.
# Optional, defines whether DHCP is enabled in specified external
# network (true by default).
externalNetworkDHCP: false
internalNetworkSecurity: true|false # Optional, true by default.
masterNodeGroup:
replicas: 3
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.large # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 50
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
# Required, volume type map for etcd and Kubernetes certificates
# (always use the fastest disk supplied by the provider).
volumeTypeMap:
# If rootDiskSize is specified, this volume type will
# be also used for master root volume.
nova: ceph-ssd
nodeGroups:
- name: front
replicas: 2
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.small # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 20
# Optional, false by default, determines if configuration drive
# is required during vm bootstrap process. It's needed
# if there is no DHCP in the network that is used as a default
# gateway.
configDrive: false
# Required, the gateway of the network will be used as the default gateway.
# Matches the cloud.prefix in the ClusterConfiguration resource.
mainNetwork: kube
additionalNetworks: # Optional.
- office
- shared
# Optional, if there are networks with disabled port
# security, their names must be specified.
networksWithSecurityDisabled:
- office
# Optional, a list of network pools where to order floating IPs.
floatingIPPools:
- public
- shared
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
# Required if rootDiskSize is specified. Volume type map for node's root volume.
volumeTypeMap:
nova: ceph-ssd
sshPublicKey: "<SSH_PUBLIC_KEY>"
provider:
...
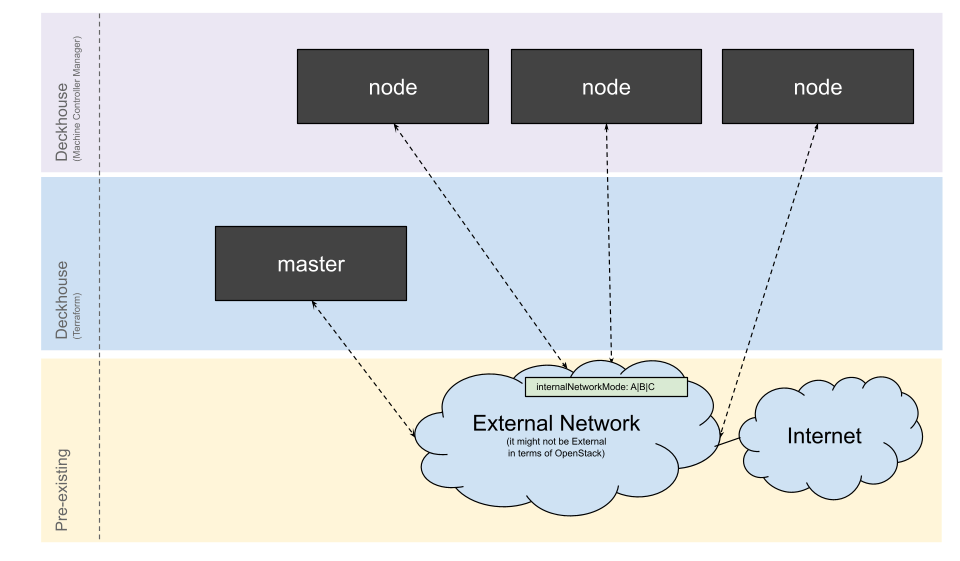
Simple
The master node and cluster nodes are connected to the existing network. This placement strategy can be useful if you need to merge a Kubernetes cluster with existing VMs.
This strategy does not support a LoadBalancer since a Floating IP is not available for the router-less network. Thus, you cannot provision a LoadBalancer with the Floating IP. An internal LoadBalancer with the virtual IP in the public network is only accessible from cluster nodes.
Example layout configuration:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: OpenStackClusterConfiguration
layout: Simple
simple:
externalNetworkName: ext-net # Required.
externalNetworkDHCP: false # Optional, true by default.
# Optional, VXLAN by default, may also be DirectRouting
# or DirectRoutingWithPortSecurityEnabled.
podNetworkMode: VXLAN
masterNodeGroup:
replicas: 3
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.large # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 50
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
# Required, volume type map for etcd and Kubernetes certificates
# (always use the fastest disk supplied by the provider).
volumeTypeMap:
# If rootDiskSize is specified, this volume type will
# be also used for master root volume.
nova: ceph-ssd
nodeGroups:
- name: front
replicas: 2
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.small # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 20
# Optional, false by default, determines if configuration drive
# is required during vm bootstrap process. It's needed
# if there is no DHCP in network that is used as a default
# gateway.
configDrive: false
# Required, the network will be used as a default gateway.
# Matches the name of the pre-created network.
mainNetwork: kube
additionalNetworks: # Optional.
- office
- shared
# Optional, if there are networks with disabled port
# security, their names must be specified.
networksWithSecurityDisabled:
- office
# Optional, list of network pools where to order floating IPs.
floatingIPPools:
- public
- shared
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
sshPublicKey: "<SSH_PUBLIC_KEY>"
provider:
...
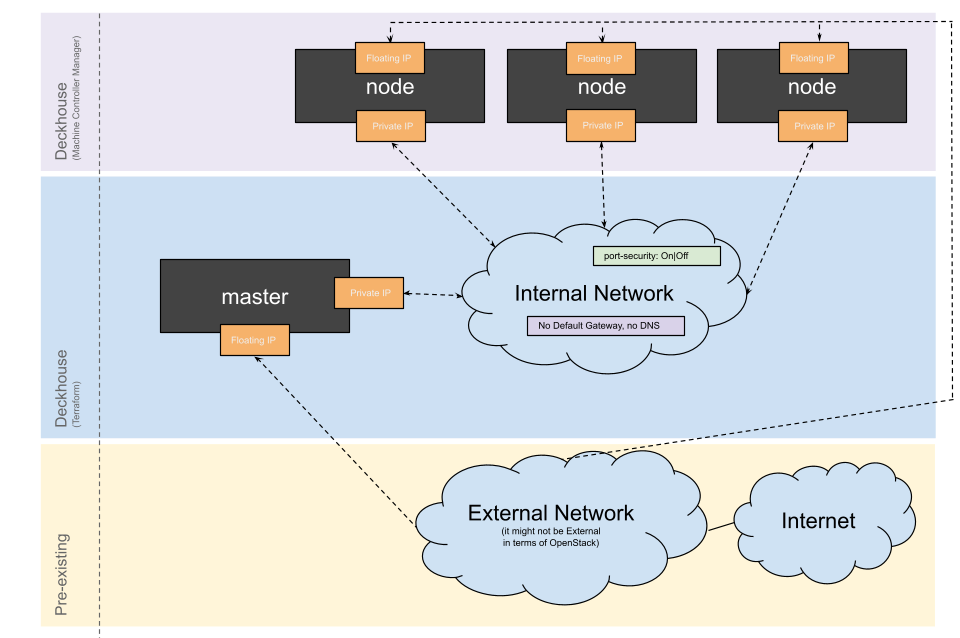
SimpleWithInternalNetwork
The master node and cluster nodes are connected to the existing network. This layout can be useful if you need to merge a Kubernetes cluster with existing VMs.
This layout does not involve the management of SecurityGroups (it is assumed they were created beforehand).
To configure security policies, you must explicitly specify both
additionalSecurityGroups in the OpenStackClusterConfiguration for the masterNodeGroup and other nodeGroups,
and additionalSecurityGroups when creating OpenStackInstanceClass in the cluster.
Example of the layout configuration:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: OpenStackClusterConfiguration
layout: SimpleWithInternalNetwork
simpleWithInternalNetwork:
# Required, all cluster nodes have to be in the same subnet.
internalSubnetName: pivot-standard
# Optional, DirectRoutingWithPortSecurityEnabled by default,
# may also be DirectRouting or VXLAN.
podNetworkMode: DirectRoutingWithPortSecurityEnabled
# Optional. If set, it will be used for the load balancer default
# configuration and ordering the master floating IP.
externalNetworkName: ext-net
# Optional, true by default.
masterWithExternalFloatingIP: false
masterNodeGroup:
replicas: 3
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.large # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 50
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
# Required, volume type map for etcd and Kubernetes certificates
# (always use the fastest disk supplied by the provider).
volumeTypeMap:
# If rootDiskSize is specified, this volume type will
# be also used for master root volume.
nova: ceph-ssd
nodeGroups:
- name: front
replicas: 2
instanceClass:
flavorName: m1.small # Required.
imageName: ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 # Required.
# Optional, local disk is used if not specified.
rootDiskSize: 20
# Optional, false by default, determines if configuration drive
# is required during vm bootstrap process. It's needed
# if there is no DHCP in the network that is used as a default
# gateway.
configDrive: false
# Required, the network will be used as a default gateway.
# Matches the name of the pre-created network.
mainNetwork: kube
additionalNetworks: # Optional.
- office
- shared
# Optional, if there are networks with disabled port
# security, their names must be specified.
networksWithSecurityDisabled:
- office
# Optional, a list of network pools where to order floating IPs.
floatingIPPools:
- public
- shared
# Optional, additional security groups.
additionalSecurityGroups:
- sec_group_1
- sec_group_2
sshPublicKey: "<SSH_PUBLIC_KEY>"
provider:
...
Configuration
Integration with Selectel is performed using the OpenStackClusterConfiguration resource. It defines the configuration of the cloud cluster in Selectel and is used by the cloud provider when the cluster control plane is hosted in the cloud. The DKP module responsible for the integration is automatically configured based on the selected layout.
To modify the configuration in a running cluster, run the following command:
d8 system edit provider-cluster-configuration
After changing node-related parameters, run the dhctl converge command to apply the changes.
The number of nodes to be provisioned and their parameters are defined in the NodeGroup custom resource,
where you also specify the name of the instance class used for that group (the cloudInstances.classReference parameter).
For the Selectel cloud provider,
the instance class is a custom resource called OpenStackInstanceClass,
which contains the specific configuration of the VMs.
When the module settings are changed, existing Machine objects in the cluster are NOT recreated (new Machine objects will use the updated parameters). The recreation only occurs if you modify the NodeGroup or the OpenStackInstanceClass parameters.
Configuration examples
The following are two simple configuration examples for the OpenStack cloud provider.
Example 1
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: OpenStackInstanceClass
metadata:
name: test
spec:
flavorName: m1.large
Example 2
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1alpha1
kind: ModuleConfig
metadata:
name: cloud-provider-openstack
spec:
version: 1
enabled: true
settings:
connection:
authURL: https://test.tests.com:5000/v3/
domainName: default
tenantName: default
username: jamie
password: nein
region: SomeRegion
externalNetworkNames:
- public
internalNetworkNames:
- kube
instances:
sshKeyPairName: my-ssh-keypair
securityGroups:
- default
- allow-ssh-and-icmp
zones:
- zone-a
- zone-b
tags:
project: cms
owner: default
List of required services
Below is the list of Selectel services required for DKP to operate in Selectel:
| Service | API version |
|---|---|
| Identity (Keystone) | v3 |
| Compute (Nova) | v2 |
| Network (Neutron) | v2 |
| Block Storage (Cinder) | v3 |
| Load Balancing (Octavia) * | v2 |
* If you need to provision a LoadBalancer.
LoadBalancer configuration
To correctly detect client IP addresses, you must use a LoadBalancer that supports Proxy Protocol.
Example: IngressNginxController
The following is a simple configuration example for an IngressNginxController:
apiVersion: deckhouse.io/v1
kind: IngressNginxController
metadata:
name: main
spec:
ingressClass: nginx
inlet: LoadBalancerWithProxyProtocol
loadBalancerWithProxyProtocol:
annotations:
loadbalancer.openstack.org/proxy-protocol: "true"
loadbalancer.openstack.org/timeout-member-connect: "2000"
nodeSelector:
node-role.deckhouse.io/frontend: ""
tolerations:
- effect: NoExecute
key: dedicated.deckhouse.io
operator: Equal
value: frontend
Node security policies and configuration
There are many reasons why you might want to restrict or allow incoming or outgoing traffic on cluster VMs. For example:
- Allow connections to cluster nodes from VMs in a different subnet.
- Allow access to specific ports on a static node for application traffic.
- Restrict access to external resources or other VMs in the cloud per security team requirements.
To manage this, you should use additional security groups. Only security groups that were pre-created in the cloud can be used.
Assigning additional security groups to static and master nodes
You can specify additional security groups either during cluster creation or in an existing cluster. In both cases, specify them in the OpenStackClusterConfiguration resource:
- For master nodes: Under the
masterNodeGroupsection using theadditionalSecurityGroupsfield. - For static nodes: Under the
nodeGroupssection of the corresponding node group configuration and also in theadditionalSecurityGroupsfield.
The additionalSecurityGroups field is an array of strings representing the names of the security groups.
Assigning additional security groups to ephemeral nodes
To assign additional security groups to ephemeral nodes,
specify the additionalSecurityGroups parameter in all relevant OpenStackInstanceClass resources used by these nodes.
Uploading an image to Selectel
-
Download the latest stable Ubuntu 18.04 image:
curl -L https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/bionic/current/bionic-server-cloudimg-amd64.img --output ~/ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 -
Prepare an openrc file that contains credentials for accessing the Selectel API.
The method of obtaining the openrc file may vary depending on the Selectel provider. If your provider offers the standard interface for Selectel, follow this guide to download the file.
-
Alternatively, install the OpenStack CLI tools following the instructions.
You can also run a container, mounting both the openrc file and the downloaded Ubuntu image:
docker run -ti --rm -v ~/ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64:/ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 -v ~/.openrc:/openrc jmcvea/openstack-client -
Initialize environment variables from the openrc file:
source /openrc -
List the available volume types:
openstack volume type listExample output:
+--------------------------------------+---------------+-----------+ | ID | Name | Is Public | +--------------------------------------+---------------+-----------+ | 8d39c9db-0293-48c0-8d44-015a2f6788ff | ko1-high-iops | True | | bf800b7c-9ae0-4cda-b9c5-fae283b3e9fd | dp1-high-iops | True | | 74101409-a462-4f03-872a-7de727a178b8 | ko1-ssd | True | | eadd8860-f5a4-45e1-ae27-8c58094257e0 | dp1-ssd | True | | 48372c05-c842-4f6e-89ca-09af3868b2c4 | ssd | True | | a75c3502-4de6-4876-a457-a6c4594c067a | ms1 | True | | ebf5922e-42af-4f97-8f23-716340290de2 | dp1 | True | | a6e853c1-78ad-4c18-93f9-2bba317a1d13 | ceph | True | +--------------------------------------+---------------+-----------+ -
Create an image and assign the volume type as a property (this is necessary if Selectel does not support local disks or they are unsuitable for workloads):
openstack image create --private --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare \ --file /ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 --property cinder_img_volume_type=dp1-high-iops ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 -
Ensure the image has been created:
openstack image show ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64Example output:
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | checksum | 3443a1fd810f4af9593d56e0e144d07d | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2020-01-10T07:23:48Z | | disk_format | qcow2 | | file | /v2/images/01998f40-57cc-4ce3-9642-c8654a6d14fc/file | | id | 01998f40-57cc-4ce3-9642-c8654a6d14fc | | min_disk | 0 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 | | owner | bbf506e3ece54e21b2acf1bf9db4f62c | | properties | cinder_img_volume_type='dp1-high-iops', direct_url='rbd://b0e441fc-c317-4acf-a606-cf74683978d2/images/01998f40-57cc-4ce3-9642-c8654a6d14fc/snap', locations='[{u'url': u'rbd://b0e441fc-c317-4acf-a606-cf74683978d2/images/01998f40-57cc-4ce3-9642-c8654a6d14fc/snap', u'metadata': {}}]' | | protected | False | | schema | /v2/schemas/image | | size | 343277568 | | status | active | | tags | | | updated_at | 2020-05-01T17:18:34Z | | virtual_size | None | | visibility | private | +------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Verifying security group support by the cloud provider
Run the openstack security group list command.
If you don’t receive any errors, it means that security groups are supported.
Configuring online volume resize
When resizing a disk via the OpenStack API, Cinder does not pass updated size information to Nova. As a result, the disk size inside the guest OS remains unchanged.
To fix this, you must configure access to the Nova API in the cinder.conf file.
For example:
[nova]
interface = admin
insecure = {{ keystone_service_internaluri_insecure | bool }}
auth_type = {{ cinder_keystone_auth_plugin }}
auth_url = {{ keystone_service_internaluri }}/v3
password = {{ nova_service_password }}
project_domain_id = default
project_name = service
region_name = {{ nova_service_region }}
user_domain_id = default
username = {{ nova_service_user_name }}
For more details, see the OpenStack-Ansible bug report.
Using rootDiskSize
Disks in Selectel
A node’s disk can be either local or network-attached. In Selectel terminology:
- A local disk is called an ephemeral disk.
- A network-attached disk is called a persistent disk (Cinder storage).
The ephemeral disk is deleted along with the VM, while the persistent disk remains in the cloud even after the VM is deleted.
- For master nodes, network-attached disks are preferred so the nodes could migrate between hypervisors.
- For ephemeral nodes, local disks are preferred for cost efficiency. However, not all cloud providers support local disks. If not supported, you have to use network-attached disks for ephemeral nodes.
| Local disk (ephemeral) | Network-attached disk (persistent) |
|---|---|
| Deleted with the VM | Remains in cloud and can be reused |
| Less expensive | More expensive |
| Suitable for ephemeral nodes | Suitable for master nodes |
rootDiskSize parameter
The OpenStackInstanceClass resource includes a rootDiskSize parameter.
In Selectel, flavors may also define a disk size.
The resulting disk type depends on the combination of the following parameters:
| flavor disk size = 0 | flavor disk size > 0 | |
|---|---|---|
rootDiskSize not set |
❗️Disk size must be specified. VM creation will fail without it. | Local disk with size from the flavor. |
rootDiskSize set |
Network-attached disk with size that equals rootDiskSize. |
❗ Both network-attached (rootDiskSize) and local (from flavor). Avoid this setup, as the cloud provider may charge for both. |
Recommendations for master nodes and bastion with network-attached disks
- Use a flavor with zero disk size.
- Set
rootDiskSizein the OpenStackInstanceClass resource. - Ensure the disk type is correct:
- If specified in the OS image, it will be used.
- If not specified, the type will be taken from
volumeTypeMap.
Recommendations for ephemeral nodes with local disks
- Use a flavor with a defined disk size.
- Do not use the
rootDiskSizeparameter in OpenStackInstanceClass. - Ensure the disk type is correct:
- If specified in the OS image, it will be used.
- If not specified, the cloud provider’s default disk type will be used.
Checking the disk size in a flavor
Run the following command:
openstack flavor show m1.medium-50g -c disk
Example output:
+-------+-------+
| Field | Value |
+-------+-------+
| disk | 50 |
+-------+-------+
Overriding the cloud provider’s default disk type
If your cloud provider offers multiple volume types,
you can specify the default type for an image by setting the cinder_img_volume_type property in the image metadata.
Any VM created from that image will use the specified volume type.
You can also create a new Selectel image and upload it.
Example:
openstack volume type list
openstack image set ubuntu-18-04-cloud-amd64 --property cinder_img_volume_type=VOLUME_NAME
Offline disk resizing
If you encounter the following error during volume resizing, reduce the number of replicas in the affected StatefulSet to 0, wait for the volume size to update, and then scale the replicas back to the original value.
Warning VolumeResizeFailed 5s (x11 over 41s) external-resizer cinder.csi.openstack.org
resize volume "pvc-555555-ab66-4f8d-947c-296520bae4c1" by resizer "cinder.csi.openstack.org" failed:
rpc error: code = Internal desc = Could not resize volume "bb5a275b-3f30-4916-9480-9efe4b6dfba5" to size 2:
Expected HTTP response code [202] when accessing
[POST https://public.infra.myfavourite-cloud-provider.ru:8776/v3/555555555555/volumes/bb5a275b-3f30-4916-9480-9efe4b6dfba5/action], but got 406 instead
{"computeFault": {"message": "Version 3.42 is not supported by the API. Minimum is 3.0 and maximum is 3.27.", "code": 406}}